In this tutorial, you will learn how to configure staking options for Hedera accounts and contracts programmatically. Perhaps you need to integrate these staking capabilities with wallets, decentralized applications, marketplaces, or other cool things you may be building on Hedera.
The article Introducing Native Staking Phase 1 on the Hedera Network
provides an overview of how staking is being rolled out on the Hedera network, so be sure to give that and HIP-406 a good read for more general information about staking.
Try It Yourself
- Get a Hedera testnet account
- This Codesandbox is already setup for you to try this example
- Fork the sandbox
- Remember to provide your testnet account credentials in the .env file
- And open a new terminal to execute accountStaking.js and contractStaking.js
- Get the example code from GitHub
Key Takeaways
If you’re a developer, here are a few key points to keep in mind about staking for accounts and contracts using the Hedera SDKs (Java, JavaScript, Go):
-
Staking options for accounts and contracts can be changed during creation or at any time by doing an account/contract update
-
The SDK classes that provide access to staking functionality are: AccountCreateTransaction(), AccountUpdateTransaction(), ContractCreateTransaction(), and ContractUpdateTransaction()
- Under these classes, the methods that enable changing staking options for accounts or contracts are: setStakedAccountId(), setStakedNodeId(), and setDeclineStakingReward()
-
setStakedAccountId() takes an account or contract ID (like 0.0.1234) as input
-
setStakedNodeId() takes a node ID (like 25) as input
-
In a single transaction, specify either setStakedAccountId() or setStakedNodeId() – NEVER specify both
-
- Hedera accounts and contracts can stake their balance to nodes, accounts, or contracts. Note that an account earns rewards only after staking to a node with declineReward=false for at least one full UTC calendar day. See HIP-406 for details.
1. Staking for Hedera Accounts
This JavaScript example performs two steps:
1.1 Create a new Hedera account and specify its staking options
1.2 Update the staking options for the account created in step 1.1
In step 1.1, Alice’s new account stakes its balance to account 0.0.2520793 and declines staking rewards. Then in step 1.2, the staking options for Alice’s new account are updated to stake to node 3 and receive staking rewards.
Here is the console output when you run the entire example:
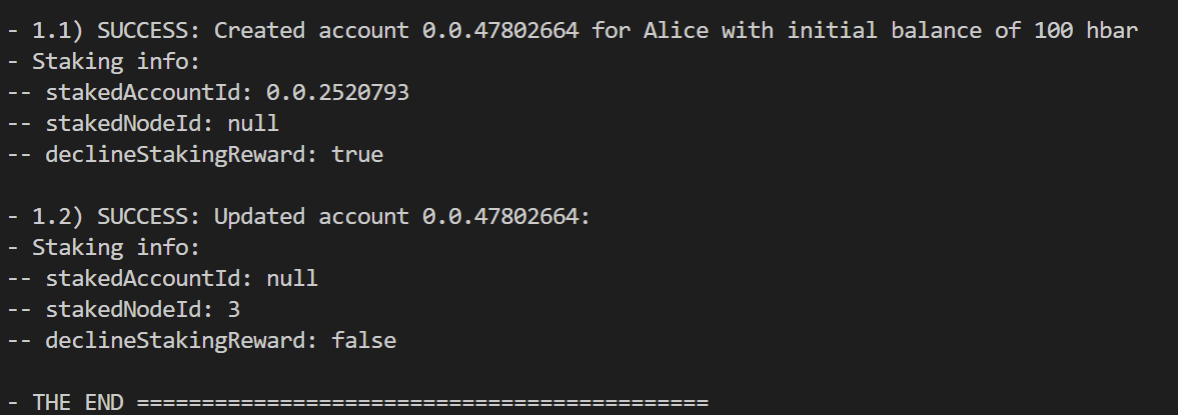
Here is the main function that implements the steps described:
async function main() {
// Create a new Hedera account
const aliceKey = PrivateKey.generateED25519();
const aliceBalance = 100;
const [accStatus, aliceId] = await accountCreatorFcn(aliceKey, aliceBalance, operatorId, true);
console.log(
`n- 1.1) ${accStatus}: Created account ${aliceId} for Alice with initial balance of ${aliceBalance} hbar`
);
await getStakingInfoFcn(aliceId);
// Update an existing account
const updateStatus = await accountUpdaterFcn(aliceId, aliceKey, 3, false);
console.log(`n- 1.2) ${updateStatus}: Updated account ${aliceId}:`);
await getStakingInfoFcn(aliceId);
console.log(`n- THE END ============================================`);
}
1.1: Staking for Newly Created Accounts
Let’s take a closer look at the function accountCreatorFcn (see below). This function creates a new Hedera account and sets its staking options. The function takes as inputs the private key and initial balance for the new account, the account ID to stake to, and a Boolean for declining or receiving the staking rewards.
Create an instance of AccountCreateTransaction() with the provided inputs and execute it using the client to create the new account. Be sure to set either setStakedAccountId() or setStakedNodeId(). Do NOT set both – the same applies for the update transaction. Note that additional method calls are commented out in case you need them in the future. The last steps are to get a transaction receipt with the Hedera client, and return the transaction status and account ID.
async function accountCreatorFcn(pvKey, iBal, stakeAccount, noRewardFlag) {
const accountCreateTx = await new AccountCreateTransaction()
.setKey(pvKey.publicKey)
.setInitialBalance(new Hbar(iBal))
.setStakedAccountId(stakeAccount) // SET THIS ONE...
// .setStakedNodeId(stakeNode) // OR THIS ONE - DON'T SET BOTH
.setDeclineStakingReward(noRewardFlag)
// .setReceiverSignatureRequired(booleanValue)
// .setMaxAutomaticTokenAssociations(amount)
// .setAccountMemo(memo)
// .setAutoRenewPeriod(autoRenewPeriod)
.execute(client);
const accountCreateRx = await accountCreateTx.getReceipt(client);
return [accountCreateRx.status, accountCreateRx.accountId];
}
1.2: Staking for Existing Accounts
The function accountUpdaterFcn user AccountUpdateTransaction() to modify properties of the Hedera account created in the previous step. The inputs for the function are the account ID to update, the private key of that account (to authorize the update), the node ID to stake to, and a Boolean for declining or receiving the staking rewards. Note that this transaction must be signed (authorized) using the private key of the account being updated. Lastly, the client submits the transaction and gets a receipt. The function returns the transaction status for the update.
Just like in the previous step, additional method calls for this class are shown and commented out in case you need them. Also, keep in mind that you can edit these functions to receive any inputs and create or update accounts according to your needs in the future.
async function accountUpdaterFcn(accountId, pvKey, stakeNode, noRewardFlag) {
const accountUpdateTx = new AccountUpdateTransaction()
.setAccountId(accountId)
// .setStakedAccountId(stakeAccount) // SET THIS ONE...
.setStakedNodeId(stakeNode) // OR THIS ONE - DON'T SET BOTH
.setDeclineStakingReward(noRewardFlag)
// .setKey(key)
// .setReceiverSignatureRequired(booleanValue)
// .setMaxAutomaticTokenAssociations(amount)
// .setAccountMemo(memo)
// .setAutoRenewPeriod(autoRenewPeriod)
// .setExpirationTime(expirationTime)
.freezeWith(client);
const accountUpdateSign = await accountUpdateTx.sign(pvKey);
const accountUpdateSubmit = await accountUpdateSign.execute(client);
const accountUpdateRx = await accountUpdateSubmit.getReceipt(client);
return accountUpdateRx.status;
}
Helper Functions
The function getStakingInfoFcn uses AccountInfoQuery() (or ContractInfoQuery() ) to get and show the staking information for the account (or contract) of interest.
async function getStakingInfoFcn(id) {
const accountInfo = await new AccountInfoQuery().setAccountId(id).execute(client);
console.log(`- Staking info:`);
console.log(`-- stakedAccountId: ${accountInfo.stakingInfo.stakedAccountId}`);
console.log(`-- stakedNodeId: ${accountInfo.stakingInfo.stakedNodeId}`);
console.log(`-- declineStakingReward: ${accountInfo.stakingInfo.declineStakingReward}`);
}
2. Staking for Hedera Smart Contracts
This JavaScript example performs two steps:
2.1 Deploy a new Hedera smart contract and specify its staking options
2.2 Update the staking options for the contract deployed in step 2.1
As shown in the console output, the contract stakes its balance to account 0.0.2520793. Even though the contract opted into receiving staking rewards, those rewards may be received by the account that the contract staked to. For details on rewards distribution scenarios, refer to HIP-406.
Then in step 2.2, the staking options for the new contract are updated to stake to node 4, but the setDeclineStakingReward flag is set to true so no rewards will be received by the contract.
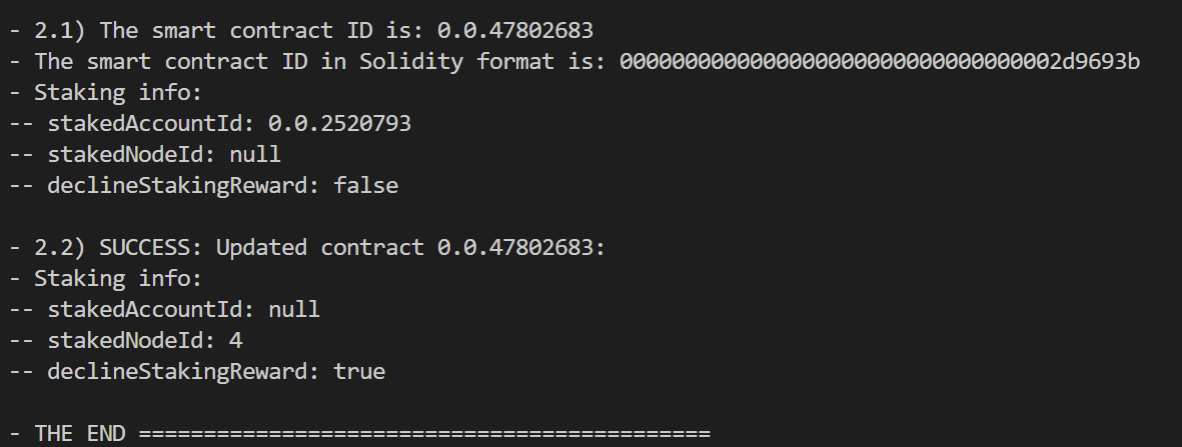
Here is the main function that implements the steps described:
async function main() {
// Import the compiled contract bytecode
const contractBytecode = fs.readFileSync("simpleContract.bin");
// Deploy a contract on Hedera
const [contractId, contractAddress] = await contractCreatorFcn(
contractBytecode,
operatorKey,
operatorId,
false
);
console.log(`n- 2.1) The smart contract ID is: ${contractId}`);
console.log(`- The smart contract ID in Solidity format is: ${contractAddress}`);
await getStakingInfoFcn(contractId);
// Update an existing smart contract (must have admin key)
const updateStatus = await contractUpdaterFcn(contractId, operatorKey, null, 4, true);
console.log(`n- 2.2) ${updateStatus}: Updated contract ${contractId}:`);
await getStakingInfoFcn(contractId);
console.log(`n- THE END ============================================`);
}
2.1: Staking for Newly Created Contracts
The function contractCreatorFcn deploys a new Hedera contract and sets its staking options. The function takes as inputs the compiled bytecode and admin key for the contract, the account ID to stake to, and a Boolean for declining or receiving the staking rewards.
Use ContractCreateFlow() to deploy the new contract with the inputs provided. Be sure to set either setStakedAccountId() or setStakedNodeId(). Do NOT set both – the same applies for the update transaction. Note that additional method calls are commented out in case you need them in the future. The last steps are to get a transaction receipt with the Hedera client and return the contract ID and contract address in Solidity format.
async function contractCreatorFcn(contractBytecode, adminKey, stakeAccount, noRewardFlag) {
const contractDeployTx = await new ContractCreateFlow()
.setBytecode(contractBytecode)
.setGas(100000)
.setAdminKey(adminKey)
.setStakedAccountId(stakeAccount) // SET THIS ONE...
// .setStakedNodeId(stakeNode) // OR THIS ONE - DON'T SET BOTH
// .setDeclineStakingReward(noRewardFlag) // MISSING IN SDK V2.17 FOR ContractCreateFlow()
// .setInitialBalance(initialBalance)
// .setConstructorParameters(constructorParameters)
// .setContractMemo(memo)
// .setAutoRenewAccountId(autoRenewAccountId)
// .setAutoRenewPeriod(autoRenewPeriod)
// .setMaxAutomaticTokenAssociations(amount)
.execute(client);
const contractDeployRx = await contractDeployTx.getReceipt(client);
const contractId = contractDeployRx.contractId;
const contractAddress = contractId.toSolidityAddress();
return [contractId, contractAddress];
}
2.2: Staking for Existing Contracts
The function contractUpdaterFcn uses the ContractUpdateTransaction() class to modify properties of the Hedera contract deployed in the previous step. The inputs for the function are the contract ID to update, the admin key of that contract (to authorize the update), the node ID to stake to, and a Boolean for declining or receiving the staking rewards. Note that this transaction must be signed (authorized) using the admin key of the contract being updated. If a contract doesn’t have an admin key, that means it’s immutable, so the staking options must be set during creation. Lastly, the client submits the transaction and gets a receipt. The function returns the transaction status for the update.
Just like in the previous step, additional methods for this class are shown and commented out in case you need them. Also, keep in mind that you can edit these functions to receive any inputs and create or update accounts according to your needs in the future.
async function contractUpdaterFcn(id, adminKey, stakeAccount, stakeNode, noRewardFlag) {
const contractUpdateTx = new ContractUpdateTransaction()
.setContractId(id)
// .setStakedAccountId(stakeAccount) // SET THIS ONE...
.setStakedNodeId(stakeNode) // OR THIS ONE - DON'T SET BOTH
.setDeclineStakingReward(noRewardFlag)
// .setAdminKey(adminKey)
// .setContractMemo(memo)
// .setAutoRenewAccountId(autoRenewAccountId)
// .setAutoRenewPeriod(autoRenewPeriod)
// .setContractExpirationTime(expirationTime)
// .setMaxAutomaticTokenAssociations(amount)
.freezeWith(client);
const contractUpdateSign = await contractUpdateTx.sign(adminKey);
const contractUpdateSubmit = await contractUpdateSign.execute(client);
const contractUpdateRx = await contractUpdateSubmit.getReceipt(client);
return contractUpdateRx.status;
}
Now you know how to stake HBAR balances for Hedera accounts and contracts upon creation and at any time by making updates to those entities. This example used the Hedera JavaScript SDK. However, you can try this with the other officially supported SDKs for Java and Go.






